1.3 Picture Representation
Several open standards were recommended to create, manipulate, store, and exchange digital images. The rules described the format of image files, the algorithms of image encoding, the form of additional information often named as metadata.
A digital image is the composition of individual pixels or picture elements. The pixels are arranged in the form of row and column to form a picture area. The number of pixels in an image is a function of the size of the image and number of pixels per unit length (e.g., inch) in horizontal as well as vertical direction.
Image Processing
It is a method to implement some operations on an image. It is also used to get an enhanced image or to access some useful information from an image. It is a type of processing in which the input is an image, and output may be the image or characteristics/features correlated with that image.
For example– photographs, frames of video.
Most image processing techniques consider the image as a two-dimensional and applying standard signal-processing technique on it.
Pixel: “Pixel is the smallest unit of a picture displayed on the computer screen.”
A pixel includes its own:-
- Intensity
- Name or Address
For example– A 2 x 2inch image and a 512 x 512 image have an aspect ratio of 1/1, whereas a 6 x 4inch image and a 1024 x 768 image have an aspect ratio of 4/3.
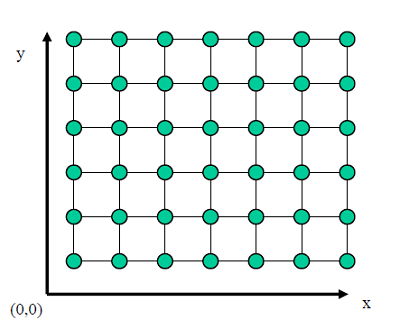
Resolution: It is the number of separate pixels display on a screen expressed in terms of pixels on the horizontal axis and vertical axis.
The sharpness of the picture on display depends on the resolution and the size of the monitor.“The number of pixels per unit is called the resolution of the image.”
It also includes-
- Image Resolution: “The distance between two pixels.”
- Screen Resolution: “The number of horizontal and vertical pixels displayed on the screen is called Screen Resolution.”
For Example– 640 x 480, 1024 x 768 (Horizontal x Vertical)
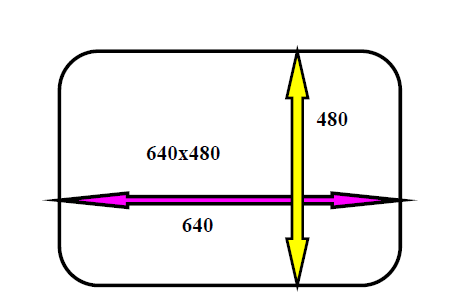
Aspect Ratio: “The ratio of image’s width to its height is known as the aspect ratio of an image.” The height and width of an image are measured in length or number of pixels.
For Example: If a graphics has an aspect ratio of 2:1, it means the width is twice large to height.
It includes–
- Frame aspect ratio: Horizontal /Vertical Size
- Pixel aspect ratio: Width of Pixel/Height of Pixel
Applications of Image Processing
Some application areas of Image Processing are as follow:
- Computerized Photography
- Space Image Processing (e.g., Hubble space telescope image, Interplanetary probe images)
- Medical/ Biological Image Processing
- Automatic Character Recognition
- Fingerprint/ Face/ Iris Recognition
- Remote sensing
- Industrial application
Format of Image Files
There are some different type of images which are mentioned as:
- JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group): It is used for digital images, especially for those images which are composed of digital photography. The ‘.jpeg’ filename extension is used to save the file.
- PNG (Portable Network Graphics): These files are commonly used to store graphics for web images. PNG was developed to enhance the non-registered replacement for Graphics Interchange Format. The ‘.png’ filename extension is used to save the file.
- GIF (Graphics Interchange Format): It is a file format for storing graphical images up to 256 colors. PNG is based on a lossless compression method, which makes higher quality output. PNG was created as a more powerful option to the GIF file format. The ‘.gif’ filename extension is used to save the file.
- TIFF/ TIF (Tagged Image File): These files can be saved in a collection of color formats and many forms of compression. TIFF file is used to maintain image integrity and clarity. It is often used for professional photography. The ‘.tif’ filename extension is used to save the file.
- PSD (Photoshop Document): It is a layered image file used in Adobe PhotoShop. It is a default format that is used by PhotoShop for saving data. PSD is a custody file that allows the user to work with the images’ separate layers even after the file has been saved. The ‘.psd’ filename extension is used to save the file.
- PDF (Portable Document Format): It is used to share the documents between computers and across operating system platforms when the user needs to save files that cannot be altered. The ‘.pdf’ filename extension is used to save the file.
- EPS (Encapsulated Postscript): It is a graphics file format, which is used in vector-based images. In Windows, the user needs graphics software to open the EPS file (i.e., Adobe Illustrator, Coral Draw). The ‘.eps’ filename extension is used to save the file.
- AI (Adobe Illustrator Document): It is a file format developed by Adobe system. It is used to represent single-page vector-based drawings in EPS or PDF formats. The ‘.ai’ filename extension is used to save the file.




